linear algebra & its applications pdf
Linear algebra’s digital resources, like PDFs from Bretscher-Otto and Nicholson, provide comprehensive coverage of core concepts and practical applications for university-level study․
Overview of Linear Algebra
Linear algebra fundamentally revolves around solving systems of linear equations, a cornerstone explored in texts like Bretscher-Otto’s “Linear Algebra with Applications․” This field delves into matrix operations, determinants, and the properties of vector spaces – concepts crucial for numerous scientific and engineering disciplines․
Importance of PDF Resources
Furthermore, PDF solutions manuals, such as those for Friedberg, Insel, and Spence’s textbook, are invaluable for self-study and reinforcing concepts․ Lyryx provides adaptable, custom editions, and open access to source files, promoting collaborative learning․ These digital formats ensure high-quality, free educational materials are widely available to students and researchers alike․

Core Concepts in Linear Algebra
Essential topics include solving linear equations, matrix operations, determinants, and vector spaces – foundational elements explored in detail within accessible PDF textbooks․
Systems of Linear Equations
Understanding systems of linear equations forms the bedrock of linear algebra, as highlighted in resources like Bretscher-Otto’s textbook․ These systems, where variables are related through linear expressions, are central to numerous applications․ The simplest case involves an equal number of unknowns and equations, providing a direct path to solutions․
PDF resources offer detailed explanations and examples of methods for solving these systems, including Gaussian elimination and matrix inversion․ Mastering this concept is crucial for progressing to more advanced topics․ The focus on solving these equations, as the starting point in many texts, emphasizes their fundamental importance in the field․ Digital access to these materials ensures free and adaptable learning․
Matrix Algebra: Operations and Properties
Matrix algebra, a core component detailed in accessible PDF formats like those by Nicholson, expands upon linear equations by introducing matrix operations․ These include addition, subtraction, multiplication, and scalar multiplication, each governed by specific properties․ Understanding these properties – associativity, distributivity, and commutativity (where applicable) – is vital for efficient calculations․
PDF resources provide step-by-step guidance on performing these operations and demonstrate their application in solving systems of equations and representing linear transformations․ The availability of adaptable and free digital texts, like those from Lyryx, facilitates a deeper grasp of these fundamental concepts․ Mastering matrix algebra unlocks further exploration within linear algebra and its diverse applications․
Determinants and their Applications
Determinants, thoroughly explained in resources like Bretscher-Otto’s “Linear Algebra with Applications” (available in PDF format), are scalar values calculated from square matrices․ These values reveal crucial information about the matrix, including invertibility – a key property for solving systems of linear equations․
PDF guides demonstrate how to compute determinants using various methods, such as cofactor expansion and row reduction․ Beyond invertibility, determinants find applications in calculating areas, volumes, and eigenvalues․ Access to free, adaptable PDF textbooks allows students to practice these calculations and understand the theoretical underpinnings․ The Friedberg, Insel, and Spence solutions manual further aids comprehension, solidifying understanding of determinant-based problem-solving․

Vector Spaces and Subspaces
Vector spaces, detailed in accessible PDFs, are fundamental to linear algebra, encompassing sets with defined addition and scalar multiplication properties․

Vector Spaces: Definition and Examples
Vector spaces form the bedrock of linear algebra, representing sets where vector addition and scalar multiplication adhere to specific axioms․ These axioms ensure predictable behavior during mathematical operations․ Examples abound, ranging from familiar Euclidean spaces (like Rn) to spaces of polynomials and functions․
Understanding vector spaces is crucial because they provide an abstract framework for solving a wide array of problems․ PDFs detailing linear algebra, such as those by Bretscher-Otto and Nicholson, meticulously define these spaces and illustrate them with numerous examples․ These resources often explore subspaces – subsets that themselves satisfy the vector space axioms, offering a hierarchical structure for analysis․ The ability to identify and work with vector spaces and subspaces is paramount for advanced applications․
Subspaces: Identifying and Properties
Subspaces are vital components within vector spaces, inheriting their properties while possessing a smaller dimension․ A subspace must contain the zero vector, be closed under vector addition, and be closed under scalar multiplication – these are the defining characteristics․ Identifying subspaces often involves verifying these conditions․
Resources like PDFs from Bretscher-Otto and Nicholson provide detailed explanations and examples of subspace identification․ Understanding their properties – such as span and linear independence – is crucial for solving linear systems and analyzing transformations․ These texts demonstrate how subspaces relate to the null space and column space of matrices, key concepts in linear algebra․ Mastering subspaces unlocks a deeper understanding of vector space structure and its applications․
Linear Transformations
Linear transformations, explored in texts like Nicholson’s, map vectors while preserving vector space structure, often represented by matrices for efficient computation and analysis․
Definition and Properties of Linear Transformations

Linear transformations are functions between vector spaces that preserve vector addition and scalar multiplication․ Formally, a transformation T: V → W is linear if T(u + v) = T(u) + T(v) and T(cu) = cT(u) for all vectors u, v in V and scalar c․
These transformations are fundamental in linear algebra, providing a way to understand how vectors change under different mappings․ Key properties include linearity, which dictates their behavior, and the ability to be represented by matrices․ Understanding these properties is crucial when applying linear algebra to fields like data science and machine learning, as transformations are used extensively in data manipulation and model building․ Resources like Bretscher-Otto’s textbook delve into these concepts with detailed explanations and examples․
Matrix Representation of Linear Transformations
Every linear transformation can be represented by a matrix․ This representation simplifies the analysis and computation of transformations․ Given a linear transformation T: V → W, where V and W are finite-dimensional vector spaces, there exists a unique matrix A such that T(x) = Ax for all x in V․

This matrix A effectively encodes the transformation’s behavior․ Utilizing matrix algebra allows for efficient composition of transformations – multiplying matrices corresponds to applying transformations sequentially․ Textbooks like Nicholson’s “Linear Algebra with Applications” (APEX Calculus) thoroughly explain this connection, providing practical methods for finding the matrix representation and applying it to solve linear systems․ This representation is vital for computational applications․

Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
Eigenvalues and eigenvectors are crucial for understanding linear transformations, revealing inherent properties of matrices and their impact on vector spaces․
Calculating Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
Determining eigenvalues involves solving the characteristic equation, det(A ⎻ λI) = 0, where A is the matrix, λ represents eigenvalues, and I is the identity matrix․ This yields a polynomial whose roots are the eigenvalues․
Once eigenvalues are found, eigenvectors are calculated by substituting each eigenvalue back into the equation (A ⎻ λI)v = 0, where v is the eigenvector․ Solving this system of linear equations provides the corresponding eigenvectors․
Resources like solutions manuals for Friedberg, Insel, and Spence’s “Linear Algebra” offer step-by-step guidance on these calculations, aiding comprehension․ Understanding these calculations is fundamental for applying linear algebra in diverse fields, including data science and machine learning, as highlighted in available PDF resources․
Applications of Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
Eigenvalues and eigenvectors are crucial in Principal Component Analysis (PCA) for dimensionality reduction in data science, identifying principal components as eigenvectors of the covariance matrix․
In machine learning, they underpin algorithms like PageRank, used by search engines, and recommendation systems, revealing the importance of nodes within networks․ Neural networks leverage these concepts for analyzing network stability and learning rates․
PDF resources, including those accompanying Bretscher-Otto and Nicholson’s textbooks, demonstrate these applications with practical examples․ Understanding these concepts, readily available in digital formats, is vital for anyone applying linear algebra to real-world problems, showcasing its power in diverse fields․
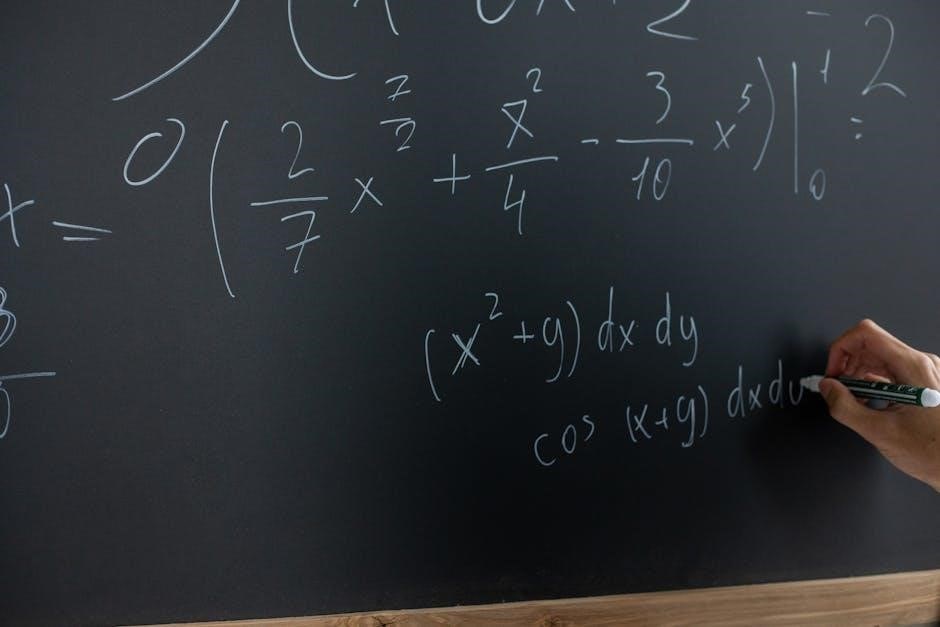
Applications of Linear Algebra
Linear algebra is fundamental to data science, machine learning, and neural networks, with accessible explanations and examples found within comprehensive PDF textbooks․
Linear Algebra in Data Science & Machine Learning
Linear algebra forms the bedrock of numerous data science and machine learning algorithms․ Understanding concepts like vector spaces, matrix operations, and linear transformations is crucial for tasks such as data dimensionality reduction, feature extraction, and model building․ PDF resources, including those by Bretscher-Otto and Nicholson, offer detailed explanations and practical examples․
These resources demonstrate how linear algebra is applied in techniques like Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Singular Value Decomposition (SVD), and regression models; Furthermore, the ability to efficiently manipulate and analyze large datasets relies heavily on the principles of linear algebra, making these PDF guides invaluable for aspiring data scientists and machine learning engineers seeking a solid theoretical foundation․
Neural Networks and Linear Algebra
Neural networks fundamentally rely on linear algebra for their operation․ Each layer within a neural network performs a series of matrix multiplications and vector additions – core linear algebra operations․ Weights are organized into matrices, and inputs are represented as vectors․ PDF resources, like those from Bretscher-Otto and Nicholson, provide the necessary mathematical background to understand these processes․
The transformation of data through neural network layers is essentially a series of linear transformations, followed by non-linear activation functions; Understanding how these linear transformations affect the data is vital for designing and training effective neural networks․ These PDF guides illuminate the connection between linear algebra and the inner workings of these powerful models․
Data Transformations using Linear Algebra
Linear algebra provides the tools for manipulating and transforming data efficiently․ Techniques like scaling, rotation, and projection are all represented by matrix operations․ PDF resources detailing linear algebra, such as those by Friedberg, Insel, and Spence, offer a solid foundation for understanding these transformations․
In data science, dimensionality reduction techniques like Principal Component Analysis (PCA) heavily utilize eigenvalues and eigenvectors – concepts thoroughly covered in linear algebra texts․ These transformations allow for simplifying datasets while preserving essential information․ Accessing PDF versions of textbooks like Bretscher-Otto’s enables a deeper grasp of these methods, crucial for effective data preprocessing and analysis․

Popular Textbooks & PDF Resources
Bretscher-Otto, Nicholson, and Friedberg, Insel, and Spence offer comprehensive linear algebra coverage, with readily available PDF resources for adaptable learning․
Bretscher-Otto: “Linear Algebra with Applications”
Bretscher-Otto’s “Linear Algebra with Applications” delivers a thorough exploration of linear algebra, skillfully blending theoretical foundations with real-world applications․ This textbook is designed for college and university students, beginning with the fundamental problem of solving linear equations, particularly focusing on scenarios where the number of unknowns matches the number of equations․
A key advantage of this resource is its complete accessibility; all digital formats are entirely FREE․ Lyryx provides adaptable custom editions and assessment tools, while also offering open access to the original source files․ This commitment to open education ensures widespread availability and encourages collaborative learning, making it a valuable asset for students and educators alike․
Nicholson: “Linear Algebra with Applications” (APEX Calculus)
Nicholson’s “Linear Algebra with Applications,” available through APEX Calculus, presents a valuable resource for students seeking a comprehensive understanding of the subject․ This book, an adaptation of a previous textbook, covers essential topics including systems of equations, matrix algebra, determinants, and vector spaces․ Notably, it has undergone a conversion from LaTeX to PreTeXt, enhancing its accessibility․
Friedberg, Insel, and Spence: “Linear Algebra” (Solutions Manual)
Friedberg, Insel, and Spence’s “Linear Algebra” offers a robust foundation in the subject, and a crucial companion to the textbook is its readily available solutions manual․ This resource is invaluable for students seeking to solidify their understanding and practice problem-solving techniques․ The solutions manual contains detailed walkthroughs for exercises found within the fourth edition of the textbook․
Access to these solutions aids in self-study and provides a means to verify one’s approach to various linear algebra problems․ While the source files for the solutions are openly available in a repository, the compiled PDF version offers a convenient and organized format for review․ This combination supports effective learning and mastery of the material․
Emerging Trends & Linear Attention
Kimi Linear, a hybrid attention architecture, surpasses traditional methods in various scenarios, utilizing chunkwise parallel form for efficient linear attention training․
Kimi Linear: A Hybrid Linear Attention Architecture
Kimi Linear represents a significant advancement in attention mechanisms, offering superior performance across short and long text sequences, as well as reinforcement learning (RL) applications․ This innovative architecture distinguishes itself by effectively combining the strengths of traditional full attention with the efficiency of linear attention methods․
At its core, Kimi Linear leverages the “Kimi Delta” approach, a key component driving its enhanced capabilities․ The chunkwise parallel form, initially proposed in “Transformer Quality in Linear Time,” is fundamental to its efficient training process․ This method enables parallel processing, drastically reducing computational demands․
Essentially, a linear layer efficiently compresses and maps high-dimensional inputs, like a 784-dimensional vector to a 10-dimensional space, acting as an intelligent filter and integrator of information․
Chunkwise Parallel Form in Linear Attention
Chunkwise parallel form is a crucial technique underpinning modern linear attention mechanisms, dramatically improving training efficiency․ Originating from the research detailed in “Transformer Quality in Linear Time,” this approach allows for the parallelization of computations, significantly reducing the time required to train large language models․
Traditional attention mechanisms suffer from quadratic complexity, making them computationally expensive for long sequences․ Linear attention, and specifically the chunkwise parallel implementation, addresses this by breaking down the input into smaller chunks․
These chunks are then processed in parallel, enabling faster training without sacrificing performance․ Currently, most linear attention training relies on this chunkwise linear layer, facilitating efficient dimensionality reduction and feature mapping․
